The risk ratio, the incidence rate ratio, and the odds ratio are relative measures of effect Risk difference is an absolute measure of effect and it is calculated by subtracting the risk of the outcome in exposed individuals from that of unexposedA rate ratio, ;After converting the odds ratio to a risk ratio, the actual risk is 14 (mortality is 14 times more likely in patients with ICU delirium compared to those without ICU delirium) Because the incidence rate in the nondelirium group is high, the odds ratio exaggerates the true risk demonstrated in

Estimating Risk
What is the difference between odds ratio and risk ratio
What is the difference between odds ratio and risk ratio- The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk is also called the risk ratio) Let's look at an example Relative Risk/Risk Ratio Suppose you have a school that wants to test out a new tutoring program RR Relative risk or RR is very common in the literature, but may represent a risk ratio, ;



1
Odds Ratios vs Risk Ratios Posted on by StatsBySlough From the previous post, we understand that Odds Ratios (OR) and Risk Ratios (RR) can sometimes, but not always be interpreted in the same way We even saw that scientific studies made the mistake of interpreting odds ratios as risk ratiosEnglishwise, they are correct it is the odds and the odds are based on a ratio calculation It is not , however, the odds ratio that is talked about when results are reported The odds ratio when results are reported refers to the ratio of two odds or, if you prefer, the ratio of two odds ratios That is, let us write Odds ratio and risk ratio are related concepts that can be interchanged when the prevalence of the effect is low, but not in other situations The realm of science is full of traps They're everywhere Neither the major medical journal, nor the most prestigious authors are free of them Many people tend to take advantage of our ignorance and
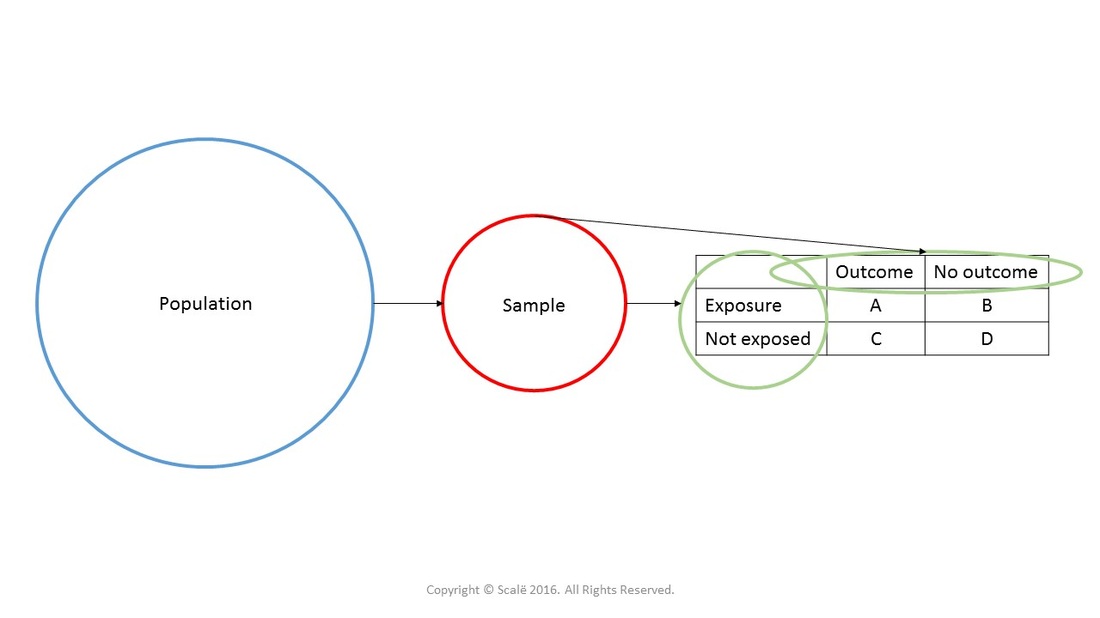
Risk (Retrospective) Menu location Analysis_Clinical Epidemiology_Risk (Retrospective) This function calculates odds ratios and population attributable risk with confidence intervals You can examine the likelihood of an outcome such as disease in relation to an exposure such as a suspected risk or protection factorAbout Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us CreatorsWe can look at the difference in risk between the two treatment groups in a different way The ratio of the risk of healing in the elastic bandage group to the risk in the inelastic bandage group is called the risk ratio For Table 4, the risk ratio = 0538/0284 = 1
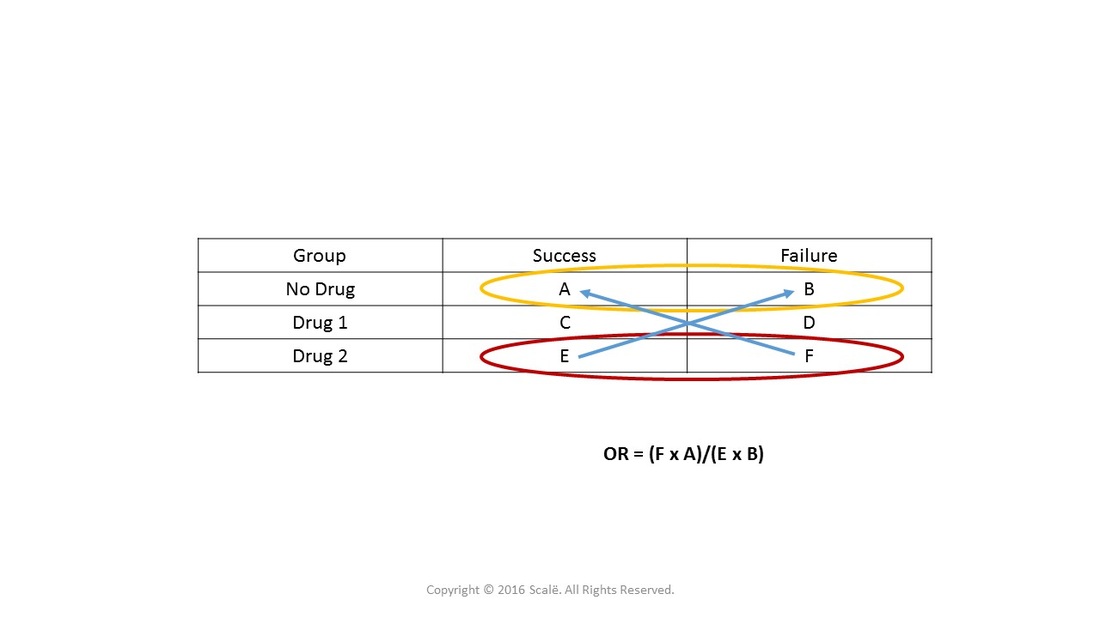
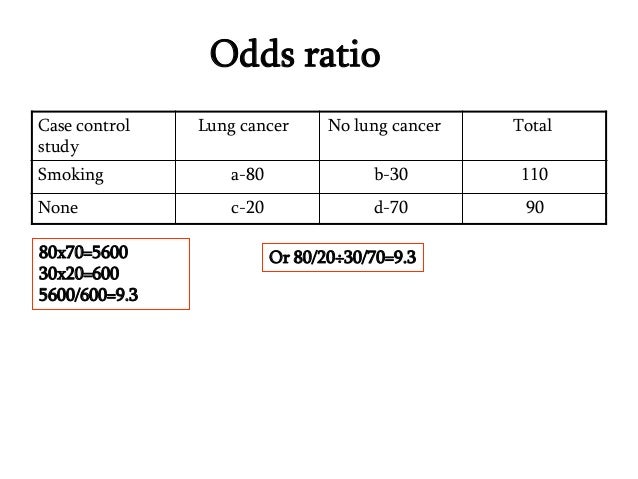
The odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of the odds of cancer in smokers to the odds of cancer in nonsmokers OR = (a/b)/(c/d) = (ad)/(bc) The risk ratio (RR), also called the relative risk, is the ratio of the probability of cancer in smokers to the probability of cancer in nonsmokersL'"odds ratio" si calcola attraverso i semplici rapporti (odds) fra le frequenze osservate e non attraverso le proporzioni Nel nostro esempio sulla urolitiasi del cane, calcoliamo gli odds (ricordati odds = p a favore / p contro) di esposizione nel gruppo dei casi e gli odds di esposizione nel gruppo dei controlli, e poi ne facciamo il rapporto A risk or odds ratio = 1 indicates no difference between the groups A risk or odds ratio > 1 indicates a heightened probability of the outcome in the treatment group The two metrics track each other, but are not equal An example with a control group and a therapy treatment group Treatment group 5 deaths, 95 survive Risk = 5/100 = 005




What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence
An odds ratio is a measure of association between the presence or absence of two properties For example, it could provide a measure of association between customers who are either older or younger than 25 and either have or have not claimed on their car insurance, in order to determine whether age is associated with the propensity to claim (the outcome of interest)For example, when the odds are 110, or 01, one person will have the event for every 10 who do not, and, using the formula, the risk of the event is 01/ (101) = 0091 In a sample of 100, about 9 individuals will have the event and 91 will notSometimes, we see the log odds ratio instead of the odds ratio The log OR comparing women to men is log(144) = 036 The log OR comparing men to women is log(069) = 036 log OR > 0 increased risk log OR = 0 no difference in risk log OR < 0 decreased risk Odds Ratio 0 5 10 15 More on the Odds Ratio Log Odds Ratio4 2 0 2 4




Converting An Odds Ratio To A Range Of Plausible Relative Risks For Better Communication Of Research Findings The Bmj



Faq How Do I Interpret Odds Ratios In Logistic Regression
Odds (failure) = q/p = 2/8 = 25 This looks a little strange but it is really saying that the odds of failure are 1 to 4 The odds of success and the odds of failure are just reciprocals of one another, ie, 1/4 = 25 and 1/25 = 4 Next, we will add another variable to the equation so that we can compute an odds ratio then the odds ratio is computed by taking the ratio of odds, where the odds in each group is computed as follows OR = (a/b) / (c/d) As with a risk ratio, the convention is to place the odds in the unexposed group in the denominatorTo measure an association with exposure, the use of prevalence ratios (PR) or odds ratios (OR) are possible In human epidemiology, much has been discussed about the use of the OR exclusively for casecontrol studies and some authors reported that there is no good justification for fitting logistic regression when the prevalence of the disease is high, in which OR overestimate the PR




Odds Ratios Vs Risk Ratios Stats By Slough




Odds Ratio Litfl Ccc Research
Odds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR) Difference Between Odds Ratio and Relative Risk Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk When two groups are under study or observation, you can use two measures to describe the comparative likelihood of an event happening These two measures are the odds ratio and relative risk Both are two different statistical concepts, although so much related to each otherRelative Risk and Odds Ratio for the obese 3) Overall, you can see that decreasing the baseline incidence will decrease the odds ratio (300 in those who are nonobese versus 129 in those who are obese) Obviously, these results run counter to expected results, putting the onus on the researcher to justify them Similarly, you should find that increasing the incidence will increase the odds ratio




Table 1 From When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar



Use And Interpret Unadjusted Odds Ratio In Spss
Inference from odds ratio If Then odds ratio = 1 the event is equally likely in both groups odds ratio > 1 the event is more likely in Group 1 odds ratio < 1 the event is more likely in Group 2 the greater the number the stronger the association In example 1 odds ratio = 36 students are much more likely to drink beer than teachers!The odds ratio can also be used to determine whether a particular exposure is a risk factor for a particular outcome, and to compare the magnitude of various risk factors for that outcome OR=1 Exposure does not affect odds of outcome OR>1 Exposure associated with higher odds of outcome ORNeither the risk ratio nor the odds ratio can be calculated for a study if there are no events in the control group This is because, as can be seen from the formulae in Box 92a, we would be trying to divide by zero The odds ratio also cannot be calculated if everybody in the intervention group experiences an event




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Glossary Of Research Terminology
RELATIVE RISK AND ODDS RATIO Risk and Odds just seemed the same to me for a long time Since then, I have come to understand to important difference Lets start with Relative Risk Relative Risk can be addressed by asking the following question How many times more likely is an "exposed" group to develop aAbsolute risk, attributable risk, attributable risk percent, population attributable risk percent, relative risk, odds, odds ratio, and others The concept and method of calculation are explained for each of these in simple terms and with the help of examples The interpretation of each is presented in plain English rather than in technical As an aside, absolute risk difference does not fix the problem in general, as sicker patients will show more absolute treatment benefit Back to odds ratios, the AB odds ratio not conditioning on patient sex is 544 Note that this is not a weighted average of 9 and 9 The unadjusted OR applies neither to males nor females



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Odds Ratio The Odds Ratio Is Used To Find The By Analyttica Datalab Medium
Not happen OR = (a/b)/ (c/d) or OR = (a × d)/ (b × c) Given the algebraic rule of cross products, the second formula will produce the same result as the other two formulae for odds ratio and is the more commonly reported formulaThe risk ratio, RR, is just the ratio of the two, which can be rewritten as In contrast, the odds of disease if exposed versus the odds of being diseased if not exposed Odds ratios While risk reports the number of events of interest in relation to the total number of trials, odds report the number of events of interest in relation to the number of events not of interest Stated differently, it reports the number of events to nonevents




Odds Ratio Calculation And Interpretation Statistics How To




Estimating Risk
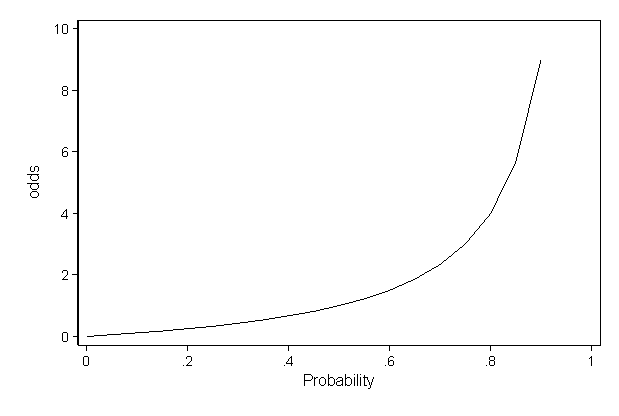
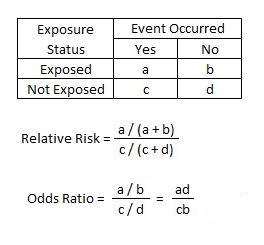
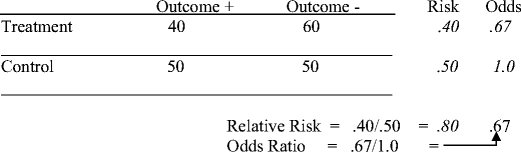
As an extreme example of the difference between risk ratio and odds ratio, if action A carries a risk of a negative outcome of 999% while action B has a risk of 990% the relative risk is approximately 1 while the odds ratio between A and B is 10 (1% = 01% x 10), more than 10 times higherDiagnostic odds ratios less than one indicate that the test can be improved by simply inverting the outcome of the test – the test is in the wrong direction, while a diagnostic odds ratio of exactly one means that the test is equally likely to predict a positive outcome whatever the true condition – the test gives no informationA risk ratio (RR), also called relative risk, compares the risk of a health event (disease, injury, risk factor, or death) among one group with the risk among another group It does so by dividing the risk (incidence proportion, attack rate) in group 1 by the risk (incidence proportion, attack rate) in
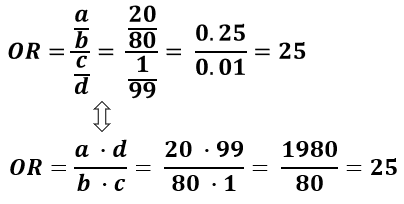



Odds Ratio Calculator Calculate Odds Ratio Confidence Intervals P Values For Odds Ratios




Odds Ratio Wikipedia
Relative Risk vs Odds ratio Relative Risk vs Odds ratio Watch later Share Copy link Info Shopping Tap to unmute If playback doesn't begin shortly, try restarting your deviceTo calculate the odds ratio, we use one of the following formulas (both give the same outcome) Example 2 We compare smokers and nonsmokers with regard to the presence of ischemic heart disease The following table shows the results Example 2 We can now calculate the odds ratio (10/40) / (5/45) = 225In the general medical literature, rate is often incorrectly used for prevalence measures




Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated




Using Odds Ratio In Case Control Studies Youtube Case Control Study Study Teaching
The relative risk (or risk ratio) is an intuitive way to compare the risks for the two groups Simply divide the cumulative incidence in exposed group by the cumulative incidence in the unexposed group where CI e is the cumulative incidence in the 'exposed' group and CI u is the cumulative incidence in the 'unexposed' group The risk of failure with SF was 96/351 (27%) vs 32/350 (9%) with HP The RR was 3 This has a very intuitive meaning risk of failure with SF was three times more likely than HP Odds Ratio The OR is a way to present the strength of association between riskOdds ratio is the likelihood that an event will occur in relation to the likelihood that an event will not occur, 1 event for and 5 events against In Gambling, the "odds" are a ratio of the likelihood of a certain outcome, related to the other outcomes I had to look this up, because I forgot this part of finite math, from 25 years ago




Confidence Intervals And P Values



Q Tbn And9gcs7g3 Oy3gxo7fbk7uvklwexnnbqcmd7m5bqd Ghq64ww9hd4dh Usqp Cau
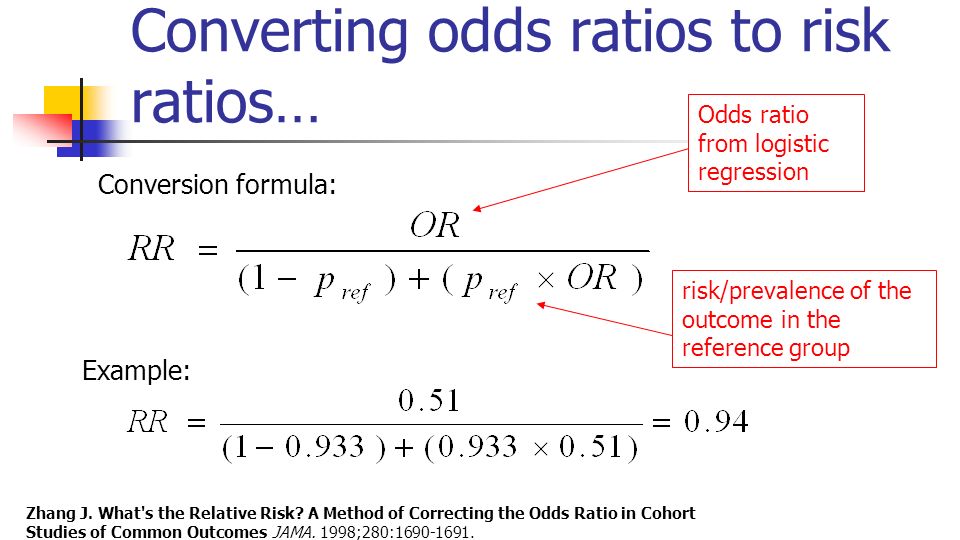
Even an odds ratio;Risk und Odds Ratio sind Begriffe, die man in der medizinischen Forschung auseinander halten sollte – vor allem, wenn man ein klinisches Paper veröffentlichen möchte „Problems arise for clinicians or authors when they interpret the odds ratio as a risk ratio, as the efficacy of protective interventions or the strength of disease determinate associations will be overestimatedLet us now look at the relation between the relative risk and the odds ratio (Zhang and Yu, 1998) OR= ˇ 1 1 1ˇ 1 ˇ 2 1 ˇ 2 = ˇ ˇ 2 1 2 1 1 = RR 2 1 (21) From this we see that OR is always further away from 1 than RR But, more importantly, we see that the odds ratio is close to the relative risk if probabilities of the outcome are small (Davies et al, 1998)




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean



Relative Risk Article
The more common the disease, the larger is the gap between odds ratio and relative risk In our example above, p wine and p no_wine were 0009 and 0012 respectively, so the odds ratio was a good approximation of the relative risk OR = 0752 and RR = 075 The Odds Ratio is a measure of association which compares the odds of disease of those exposed to the odds of disease those unexposed Formulae OR = (odds of disease in exposed) / (odds of disease in the nonexposed)Relative Risk (RR) is a ratio of probabilities or put another way it is one probability divided by another Odds Ratio (OR) is a ratio or proportion of odds I just remember that odds ratio is a ratio of odds and probability isn't a ratio of odds (AKA it is the other option) Relative Risk = Probability /




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Kidney International




상대위험도 Relative Risk Vs 오즈비 Odds Ratio
There can be substantial difference in the association of a risk factor with prevalent disease versus ;Relative Risk, Odds, Now we can't calculate the Relative Risk of dying from lung cancer if you're a smoker vs a nonsmoker But the Odds ratio still works, and we can easily calculate it 9,333 x 5,003 Here's a formula (for 2 x 2 tables) # of ways of # of ways ofDe odds ratio is de verhouding tussen twee wedverhoudingen of oddsDaarbij is de wedverhouding de verhouding tussen de waarschijnlijkheid dat een gebeurtenis optreedt (zal optreden) en de waarschijnlijkheid dat ze niet optreedt (zal optreden) Zou bijvoorbeeld bij een positief testresultaat 1000 keer een ziekte B vastgesteld zijn en 100 keer de afwezigheid van ziekte B, dan is de




How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube
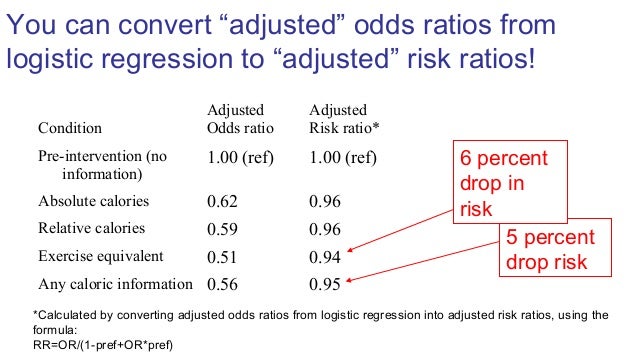



Math3010 Week 6
Odds ratio (OR) and risk ratio (RR) are two commonly used measures of association reported in research studies In crosssectional studies, the odds ratio is also referred to as the prevalence odds ratio (POR) when prevalent cases are included, and, instead of the RR, the prevalence ratio (PR) is calculatedA prevalence ratio, or ; Once we calculate the odds ratio and relative risk, we may also be interested in computing confidence intervals for these two metrics A 95% confidence interval for the odds ratio can be calculated using the following formula 95% CI for odds ratio = exp(ln(OR) – 196*SE(ln(OR))) to exp(ln(OR) – 196*SE(ln(OR)))
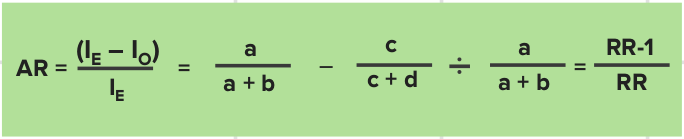



Attributable Risk And Odds Ratio Online Medical Library




Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training




The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology




Assessment Of Multiplicative Interaction Using Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios Download Scientific Diagram




Absolute Relative And Attributable Risks Outcomes Or Differences That We Are Interested In Differences In Means Or Proportions Odds Ratio Or Ppt Download



27 Sep 01 Draft




Odds Ratio Wikipedia
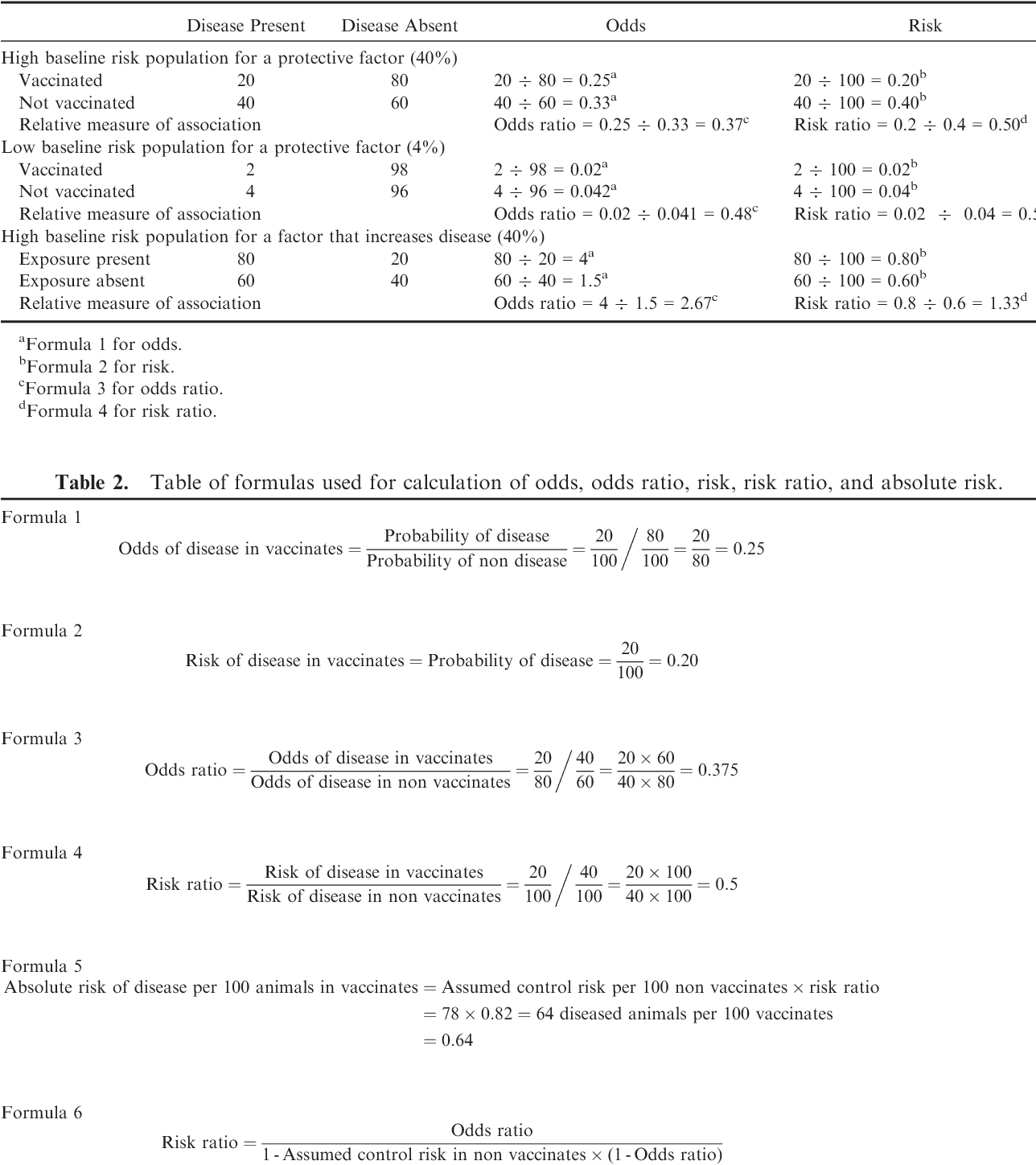



Table 2 From Interpretation Of Odds And Risk Ratios Semantic Scholar




Calculation Of Odds Ratios Or And Relative Risk Rr Derived From Download Scientific Diagram




View Image




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Kidney International




Calculation Of Ror Reporting Odds Ratio Contingency Table And Formula Download Scientific Diagram



Introduction To Genetic Epidemiology Lesson 5 Analyzing The Data




Odds Ratio Wikipedia



1
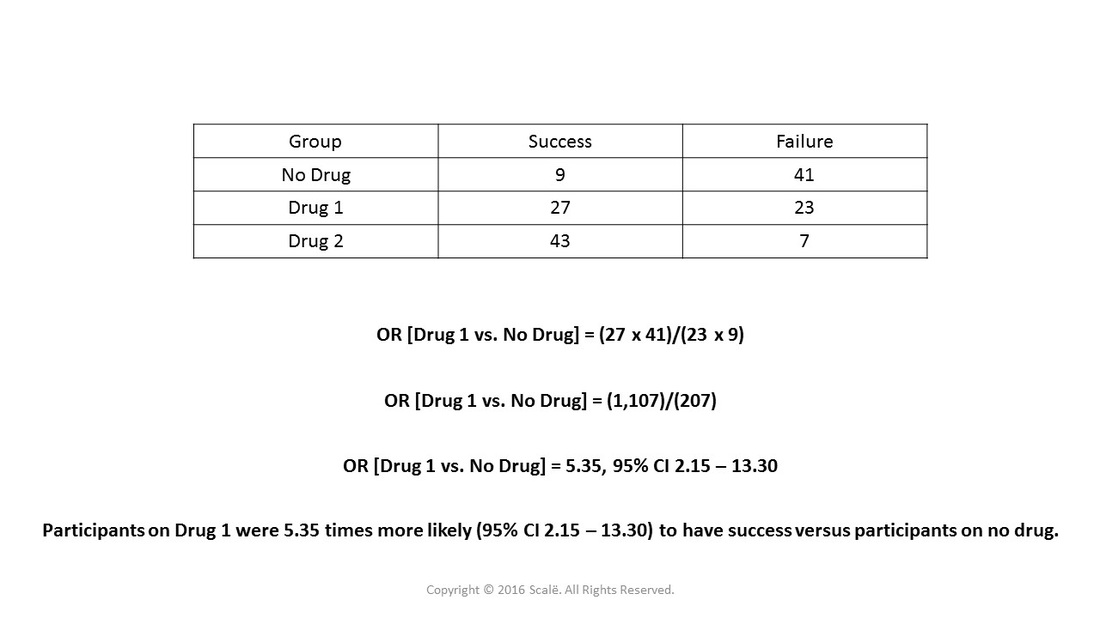



Use And Interpret Unadjusted Odds Ratio In Spss
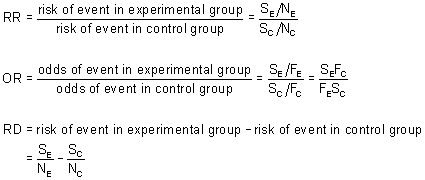



Box 9 2 A Calculation Of Rr Or And Rd




Statistics Part 13 Measuring Association Between Categorical Data Relative Risk Odds Ratio Attributable Risk Logistic Regression Data Lab Bangladesh




Youll Need To Know Prevalence Rate Odds Ratio Chegg Com




Calculation Of Relative Risks Rr And Odd Ratios Or Download Table




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology



Estimating Risk
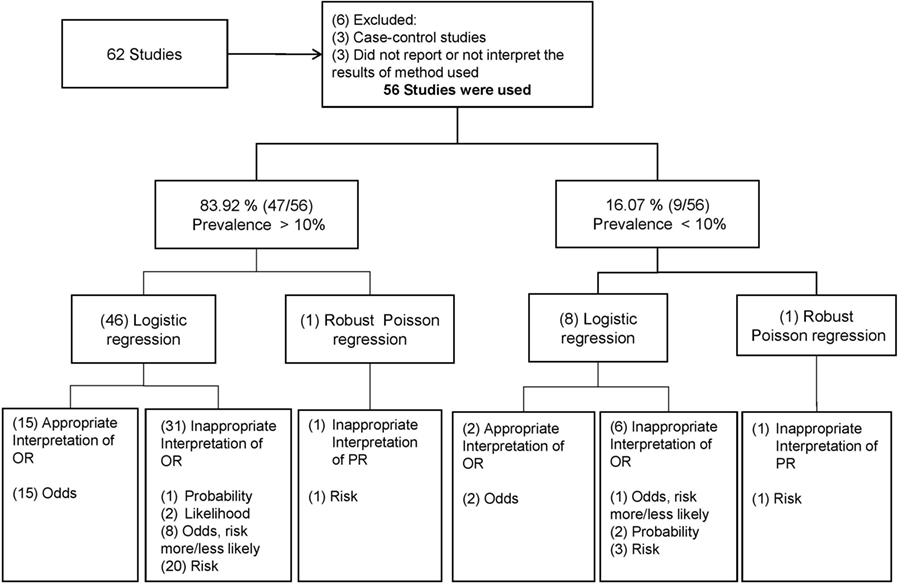



Frontiers Odds Ratio Or Prevalence Ratio An Overview Of Reported Statistical Methods And Appropriateness Of Interpretations In Cross Sectional Studies With Dichotomous Outcomes In Veterinary Medicine Veterinary Science




Calculating The Risk Ratio Odds Ratio And Risk Difference In A Randomised Controlled Trial Youtube




Lecture3



Relative Risk Odds Ratio




A Focused 08 Update On Methods For Cochrane




Using Odds Ratio In Case Control Studies Youtube




Understanding Systematic Reviews And Meta Analysis Archives Of Disease In Childhood




Calculation Of Odds Ratios Or And Relative Risk Rr Derived From Download Scientific Diagram




Measuring Of Risk



Calculate Odds Ratio With 95 Confidence Intervals




Odds Ratio Article




Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube




When Can Odds Ratios Mislead The Bmj




Effect Sizes Basicmedical Key




Odds Ratios The Odd One Out Stats By Slough




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology




Random And Systematic Errors In Case Control Studies Calculating The Injury Risk Of Driving Under The Influence Of Psychoactive Substances Sciencedirect




12 Biostats Ideas Regression Analysis Linear Regression Chi Square




Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated



Statistics In Medicine Ppt Download



Risk Ratio Vs Odds Ratio Hunter 19 Notes And Things




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Calculation And Interpretation Of Odds Ratio Or And Risk Ratio Rr Youtube




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal




How To Calculate An Odds Ratio Youtube



Tips For Teachers Of Evidence Based Medicine Understanding Odds Ratios And Their Relationship To Risk Ratios Springerlink




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Moving Beyond Odds Ratios Estimating And Presenting Absolute



Q Tbn And9gcs Pnxsjy3 X0gf842wm6tcfnesq2htc0kvu Tt2rst Svunqcb Usqp Cau




On Biostatistics And Clinical Trials Odds Ratio And Relative Risk
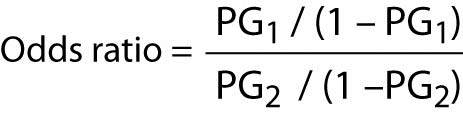



The Odds Ratio Calculation Usage And Interpretation Biochemia Medica




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology
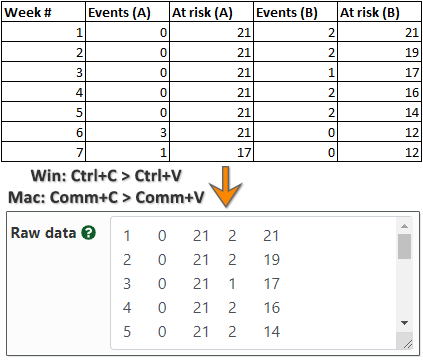



Hazard Ratio Calculator Calculate Hazard Ratio Hr Confidence Intervals P Value



Meta Analysis Is A Summary Analysis Of More Studies Ecstep




Interpreting Odds Ratio Senguptas Research Academy



Confluence Mobile Wiki Ucsf



Relative Risk Wikipedia



Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios




Frontiers Odds Ratio Or Prevalence Ratio An Overview Of Reported Statistical Methods And Appropriateness Of Interpretations In Cross Sectional Studies With Dichotomous Outcomes In Veterinary Medicine Veterinary Science




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 Review 1 Similar To The Risk Ratio Here Are The Guidelines For Calculating A Confidence Interval For 2 Independent Samples And The Odds Ratio As The Parameter Of Interest 2 Note That Calculation Of The Confidence




In A Meta Analysis Of Adjusted Estimates From Observational Studies Can I Pool Or With Hr And Rr Probably Not How Can I Transform Hr To Or




Risk Ratio



Q Tbn And9gcr Ttka12jaocnx Gn3ox9ci1ggq18vcw9359i6hq2cschyusam Usqp Cau
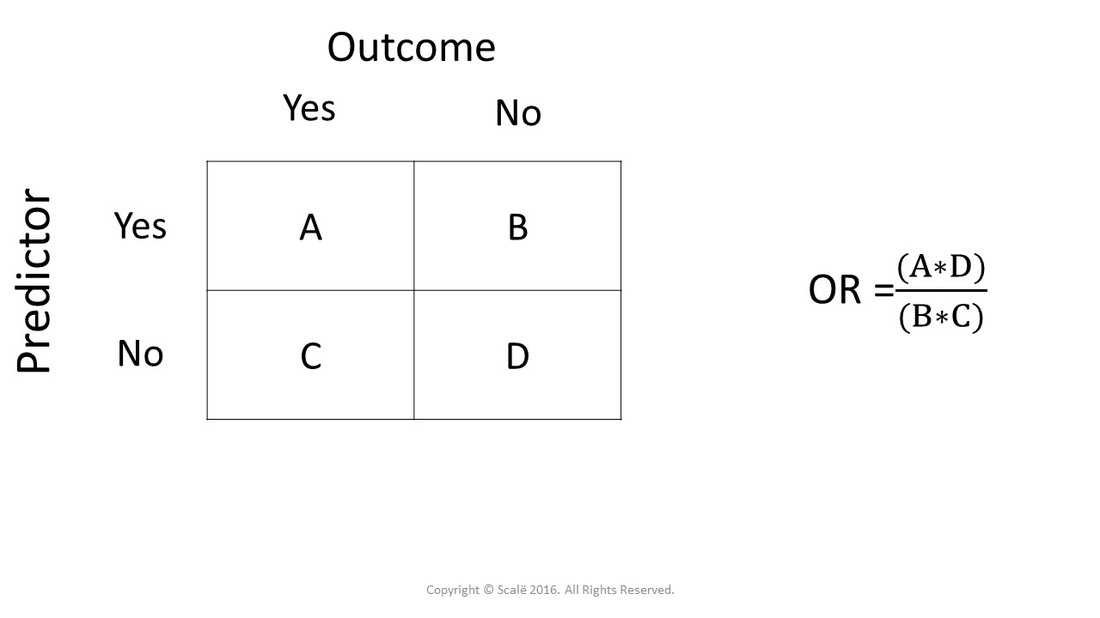



Calculate Odds Ratio With 95 Confidence Intervals




Risk Differences And Rate Differences
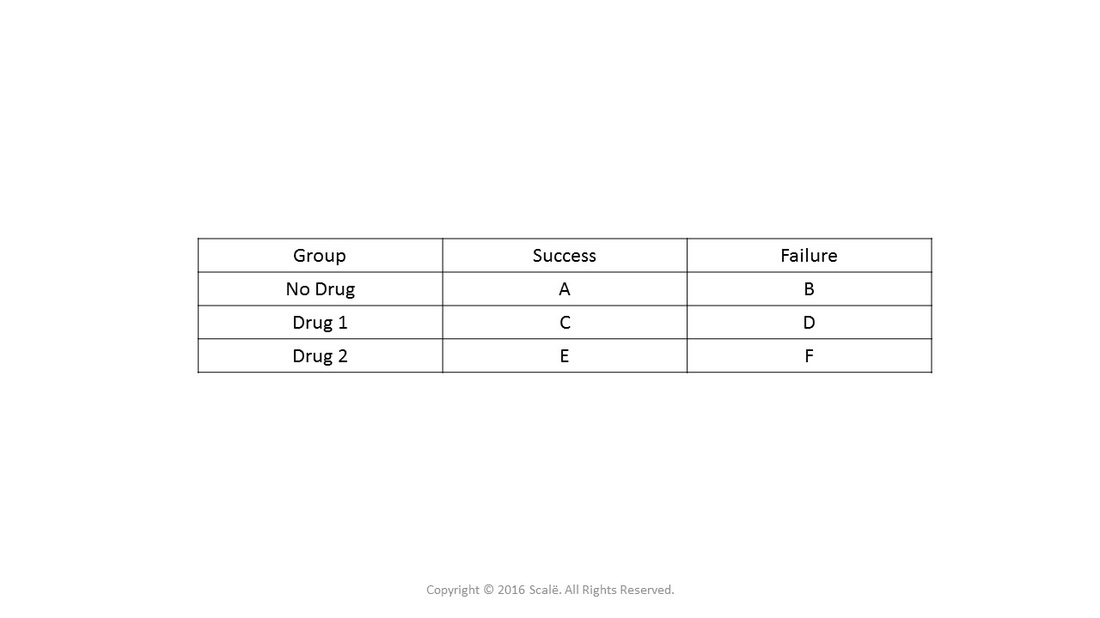



Use And Interpret Unadjusted Odds Ratio In Spss




Xmlinkhub




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Calculation Definition Probability Odds Youtube




Or Rr Pdf Pdf Relative Risk Odds Ratio




Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Usmle The Journey



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿