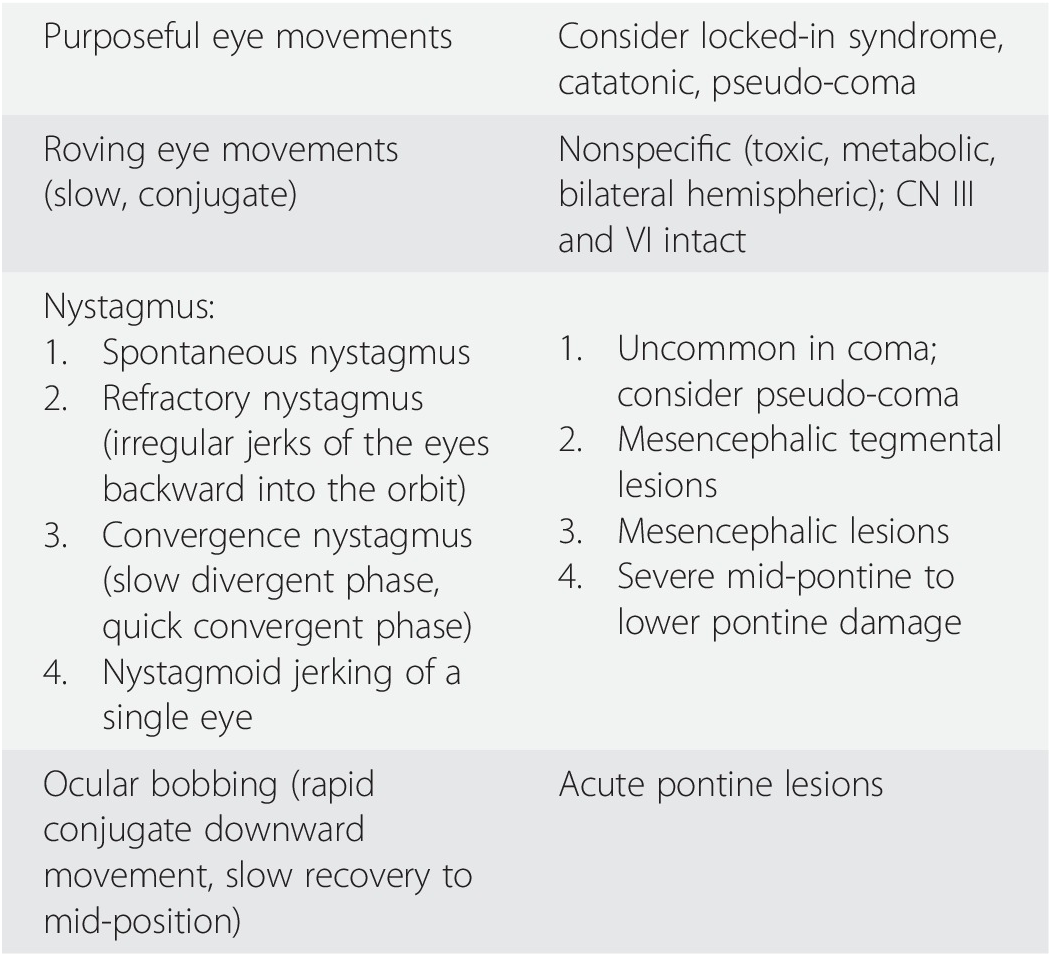
The awake patient's eyes move concomitantly with head rotation when assessing the oculocephalic reflex It is nearly impossible for an awake patient to mimic the brainstem oculocephalic responses of a truly comatose patient on cold caloric testing the patient may wake up or exhibit preservation of the fast component of nystagmus MotorMouth Care Procedure for Unconscious Patient Arrange all equipment on the bedside cabinet or an overbed table Set the patient's bed in a comfortable position and lower one side rail Place a bulb syringe or suction machine with a suction machine nearby Place the client in a sidelying positionComa is a presenting symptom in approximately 051% of emergency department admissions, although the only paper addressing frequency of coma in the ED dates from 1934, citing coma as the presentation in 3% of admissions to the ED A more recent retrospective analysis found alteration of mental status in between 4% and 10% of ED patients Disturbances may be caused by a wide variety of

Sleeping Positions What S The Best Sleeping Position
Position of comatose patient
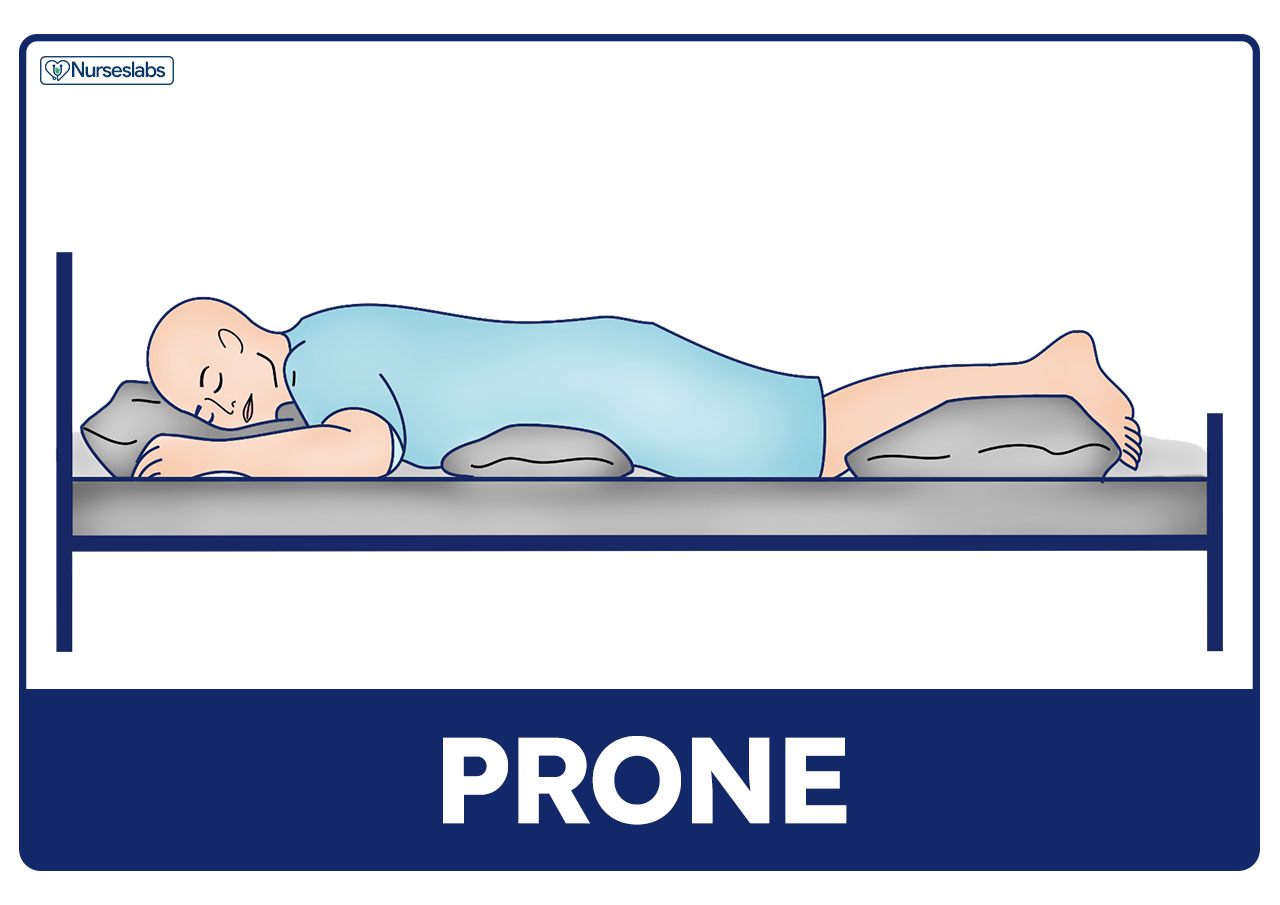
Position of comatose patient-You can use the same supine position, but elevate the head of the bed to around 80 to 90 degrees Support the patient's back with the placement of few pillows Support the affected shoulder with an arm tray or a bedside table You can use a pillow on the arm tray to provide an extra cushion as well as to bring the shoulder in neutralSupine position Prone position Patient lies on stomach with head turned to the side Prone position Lateral position Patient lies on the side of the body with the top leg over the bottom leg This position helps relieve pressure on the coccyx Lateral position Sims position Patient lies between supine and prone with legs flexed in front of the patient



Patient Positioning Cheat Sheet
Coma Coma is a state of unconsciousness caused by temporary or permanent impairment of the ascending reticular system in the brainstem, or both cerebral hemispheres The key components of the neurological examination of the comatose patient are level of consciousness (Glasgow Coma Score — list the components;T he neurologist is often required to evaluate the unconscious patient from both the diagnostic and prognostic perspective Knowledge of the anatomical basis of coma is essential for competent evaluation but must be combined with an understanding of the many, often multifactorial, medical conditions that result in impaired consciousnessA Head of bed elevated at least 30° with the affected arm elevated on a pillow B Forward sidelying position
Following are guidelines for improving the arousal of the comatose patients Approaching the Patient • Make the patient identify you • Talk to the patient slowly and in a normal tone of voice • Keep sentences short and give the patient extra time to think about what you have said and repeat it a few timesA Paralysis (Partially correctPatients who might be at higher risk for skin breakdown include stroke victims, diabetic neuropathy, comatose or paralyzed patients, patients with casts or braces, Alzheimers or dementia, confused or depressed patients, postsurgical patients, patients with blood flow problems,Eg E4V5M6 = GCS 15)
What is the correct position?Which is the best position in which she should place the client?'A state of profound unconsciousness caused by disease, injury, or poison The patient is unresponsive and cannot be roused' It may be a transient phenomenon during acute illness or persist in the long term Patients in a coma are alive yet unable to perceive or react meaningfully to their external environment


Patient Positioning Sims Orthopneic Dorsal Recumbent Guide


Recovery Position Wikipedia
Coma is a state of unconsciousness caused by temporary or permanent impairment of the ascending reticular system in the brainstem, or both cerebral hemispheres The key components of the neurological examination of the comatose patient are level of consciousness (Glasgow Coma Score — list the components;In catalepsy, volition and consciousness are interrupted while the limbs remain in the same position Among the genus of lethargus, again six species were distinguished, including Lethargus à narcoticis The patient can be easily awoken, responds to questions and may move important observations on comatose patients had been made TheLawyers for the comatose woman who was raped and later gave birth at Hacienda Healthcare in Phoenix, Arizona have said she was raped repeatedly and may have been impregnated before



Coma Usmf



Airway Establishment And Control Critical Care Medicine Merck Manuals Professional Edition
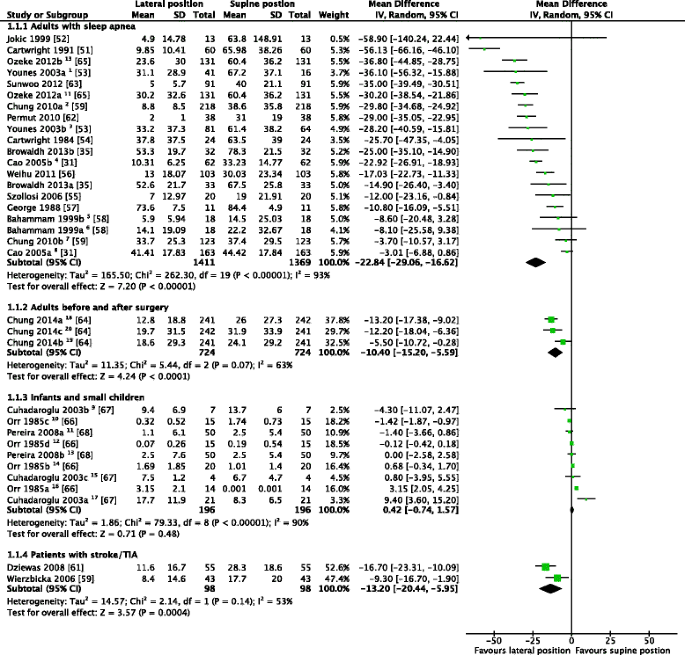
A patient who is comatose, experiences spasticity, has extensive paralysis, or is unable to mentally or physically maintain a safe position may require some form of temporary restraint or protective positioning These protective measures are to be differentiated from the use of restraints for a prolonged periodA brief reminder of proper patient turning and repositioning techniquesObjective The left lateral decubitus position is generally accepted as the position of choice to protect against aspiration pneumonia in comatose poisoned patients We studied the relationship between initial body position during coma and subsequent development of suspected aspiration pneumonia (SAP) Design Observational, descriptive study


Is The Supine Position Associated With Loss Of Airway Patency In Unconscious Trauma Patients A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Scandinavian Journal Of Trauma Resuscitation And Emergency Medicine Full Text



Pdf Postraumatic Ards How To Place Patients Who May Offer Technical Problems In A Prone Position
A brief reminder of proper patient turning and repositioning techniquesCombine this with the reclining position of comatose patients, the fact that normal digestive processes are slowed in the unconscious and the danger that feedings divorced from hunger signals mayMental status is evaluated by observing the patient's response to visual, auditory and noxious (ie, painful) stimuli The three main maneuvers to produce a noxious stimulus in a comatose patient are 1 press very hard with your thumb under the bony superior roof of the orbital cavity, 2 squeeze the patient's nipple very hard, and 3 press a pen hard on one of the patient's fingernails Comatose patients may demonstrate motor responses indicative of more generalized reflexes



Podcast 124 The Logistics Of Proning For Ards



Facts About Vegetative And Minimally Conscious States After Severe Brain Injury Page 3 Brainline
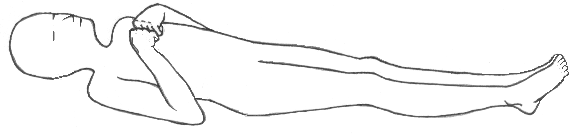
The patient begins in the supine position and is rolled onto the side (the operative side is up) The patient's bottom leg should be flexed, and the top leg straight with a pillow in between the legsA position in which the patient is placed on the left side with the left arm moved aside and supported to allow for lung expansion and the right leg crossed over the left This position affords the unconscious, breathing patient the best protection from airway occlusion or aspiration of fluids into the lungsIt is an eye's reflex movement test, to estimating the brain functioning in comatose or servery lethargic patients The word "doll's eye" somehow can be correlated to toy dolls that have mechanical eye function ie even with the movement of their head, their eyes where fixed at a position and seems to move opposite to the direction of


Teen Explains What Life Is Like In A Coma Abc News


How To Perform A Lumbar Puncture
Caregivers of a person who is in coma or recently recovering from a coma, they may have many concerns and questions in trying to cope with a serious illness This guide was developed as a result of the need we identified, when our 29yearold daughter, Jill Elizabeth Russell Eddy was in coma for 12 monthsCheyneStokes breathing is an abnormal pattern of breathing commonly seen as patients approach death(A medically induced coma, by contrast, ends when the drugs that are inducing the coma are cut off, thus arousing the patient) Comas are by definition states from which you can't be aroused
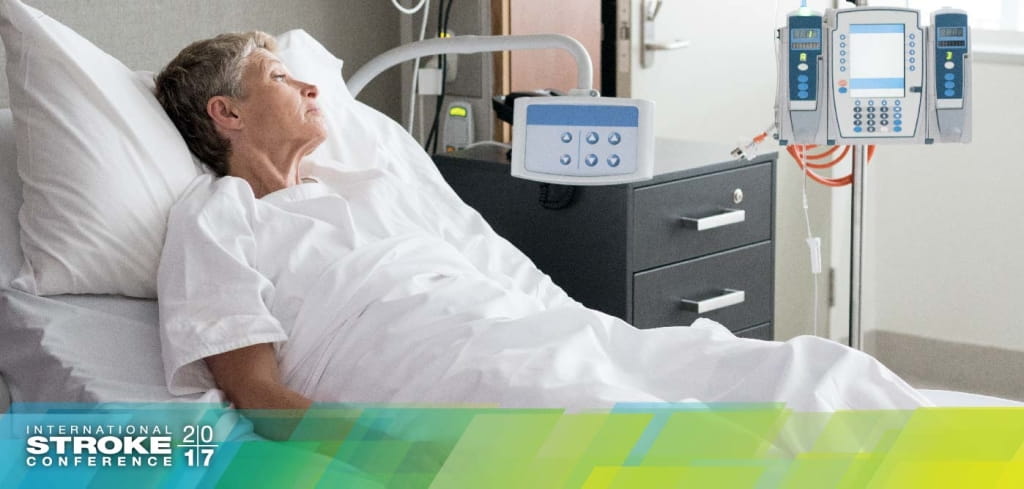



Head Position After Stroke Up Or Down American Heart Association



File Coma Position Jpg Wikimedia Commons
A patient who awakens from a coma may also develop a socalled lockedin syndrome, being completely conscious but paralyzed and unable to communicate, except through eye blinks So the differenceA patient who is comatose, experiences spasticity, has extensive paralysis, or is unable to mentally or physically maintain a safe position may require some form of temporary restraint or protective positioning These protective measures are to be differentiated from the use of restraints for a prolonged periodAltered levels of consciousness, such as when a patient is lethargic or comatose, for example, can also impair a patient's ability to clear his or her airway Thus, the patient's secretions build up and cause a loud, rattling sound when air passes through the airway


Respiratory Arrest Wikipedia
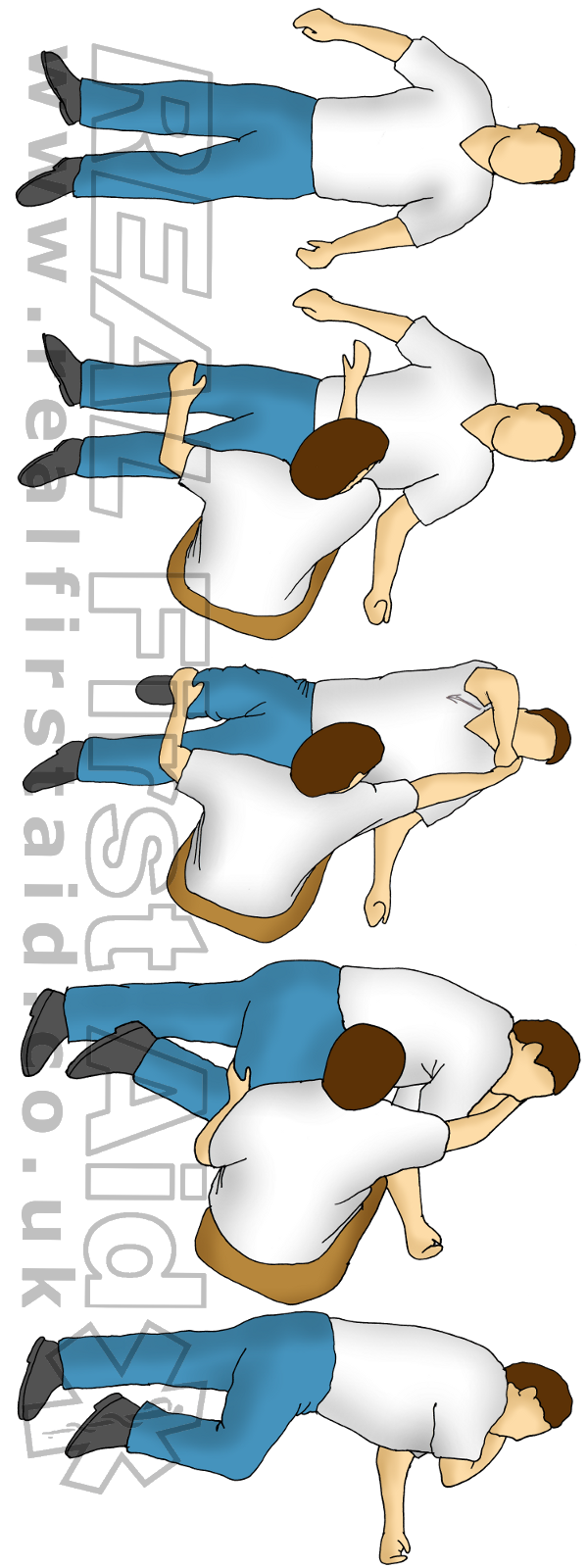


Casualty Positioning Real First Aid
Swing the patient's feet off the edge of the bed and move them into a sitting position Place 1 arm under the patient's shoulders and 1 arm behind their knees Bend your knees as you swing the patient's feet off the edge of the bed Shift your weight to your back foot and gently ease them into an upright sitting position, facing youThe patient's air passages must be kept open so that he will be guaranteed a proper exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide Even if the lumen of the trachea is not partially narrowed by pillows placed under his head, the comatose patient should not be allowed to lie on his back as this position is unfavorable to adequate pulmonary ventilationTreatment for a coma depends on the cause People close to the comatose patient should give doctors as much information as possible to help the doctors determine the cause of coma Prompt medical



Glasgow Coma Scale Gcs How To Assess Gcs Geeky Medics



Decorticate Posturing Symptoms And Causes
Eg E4V5M6 = GCS 15)A fully conscious patient has a Glasgow Coma Score of 15 A person in a deep coma has a Glasgow Coma Score of 3 (there is no lower score) The Rancho Level of Cognitive Functioning Scale (LCFS) is a scale used to assess cognitive functioning in people with brain injury 11 The first three levels are similar to the stages of coma, VS, and MCS This scale is most often used in the first yearWell that depends on the nature of injury or illness that resulted in the person being in a coma If there is a hemiplegia (paralysis of one side) the position is to normalise muscle tone and maintain range of movement If there are fractures, the positioning becomes complicated but still important



Position Of The American Dietetic Association Journal Of The American Dietetic Association



6 A Patient With Multiple Sclerosis Spends Most Of The Day In A Wheelchair Or Bed Homeworklib
A Paralysis (Partially correctPatients who might be at higher risk for skin breakdown include stroke victims, diabetic neuropathy, comatose or paralyzed patients, patients with casts or braces, Alzheimers or dementia, confused or depressed patients, postsurgical patients, patients with blood flow problems,The awake patient's eyes move concomitantly with head rotation when assessing the oculocephalic reflex It is nearly impossible for an awake patient to mimic the brainstem oculocephalic responses of a truly comatose patient on cold caloric testing the patient may wake up or exhibit preservation of the fast component of nystagmus MotorA "When patients are placed or fall into a coma, the eyelids are usually closed or in close apposition," says Andrew S Gurwood, OD, of Pennsylvania College of Optometry at Salus University In this state, Bell's phenomenon (when the eyes reflexively roll upward under the upper eyelid for protection from drying and foreign matter) may



Patient Positioning Sims Orthopneic Dorsal Recumbent Guide



Coronavirus How Physiotherapists Are Helping Patients Recover
Treatment by default, because of a lack of consideration of the patient's wishes, and a lack of will or courage to find alternatives, is not an acceptable ethical position Treatment ComaPosition Positioning the patient to maximize venous outflow from the head can help minimize increases in ICP The head of the bed can be elevated to 30° (with the head above the heart) as long as cerebral perfusion pressure remains at the desired rangeEmergency Management of the Comatose Patient As with any medical emergency, establishment of an airway is paramount Any patient with a GCS of less than 9 should undergo intubation Patients should be placed on oxygen and fully undressed If there is any suspicion of cervical spine (Cspine) injury, the Cspine should be immobilized



First Aid For Unconsciousness Symptoms Treatment Causes More



Sitting Position Improves Consciousness Level In Patients With Cerebral Disorders
In first aid, the recovery position (also called semiprone) refers to one of a series of variations on a lateral recumbent or threequarters prone position of the body, often used for unconscious but breathing casualties An unconscious person, a person who is assessed on the Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) at eight or below, in a supine position (on the back) may not be able to maintain an open airway as a conscious person wouldHemilithotomy Position The patient's nonoperative leg is positioned in standard lithotomy TheMental status is evaluated by observing the patient's response to visual, auditory and noxious (ie, painful) stimuli The three main maneuvers to produce a noxious stimulus in a comatose patient are 1 press very hard with your thumb under the bony superior roof of the orbital cavity, 2 squeeze the patient's nipple very hard, and 3 press a pen hard on one of the patient's fingernails Comatose patients may demonstrate motor responses indicative of more generalized reflexes



Patient Positioning Sims Orthopneic Dorsal Recumbent Guide



Coma Wikipedia
Among patients put in the prone position, there was no difference in intubation rate between patients who maintained improved oxygenation (ie, responders) and nonresponders 9 A prospective, multicenter observational cohort study in Spain and Andorra evaluated the effect of prone positioning on the rate of intubation in COVID19 patients withThe patient has no gag reflex The movement of the breathing tube (in and out) or the insertion of a smaller tube down the breathing tube will cause a gag reflex in a comatose patient, but will not elicit a reflex in the braindead patient The patient has no spontaneous respirationT he neurologist is often required to evaluate the unconscious patient from both the diagnostic and prognostic perspective Knowledge of the anatomical basis of coma is essential for competent evaluation but must be combined with an understanding of the many, often multifactorial, medical conditions that result in impaired consciousness
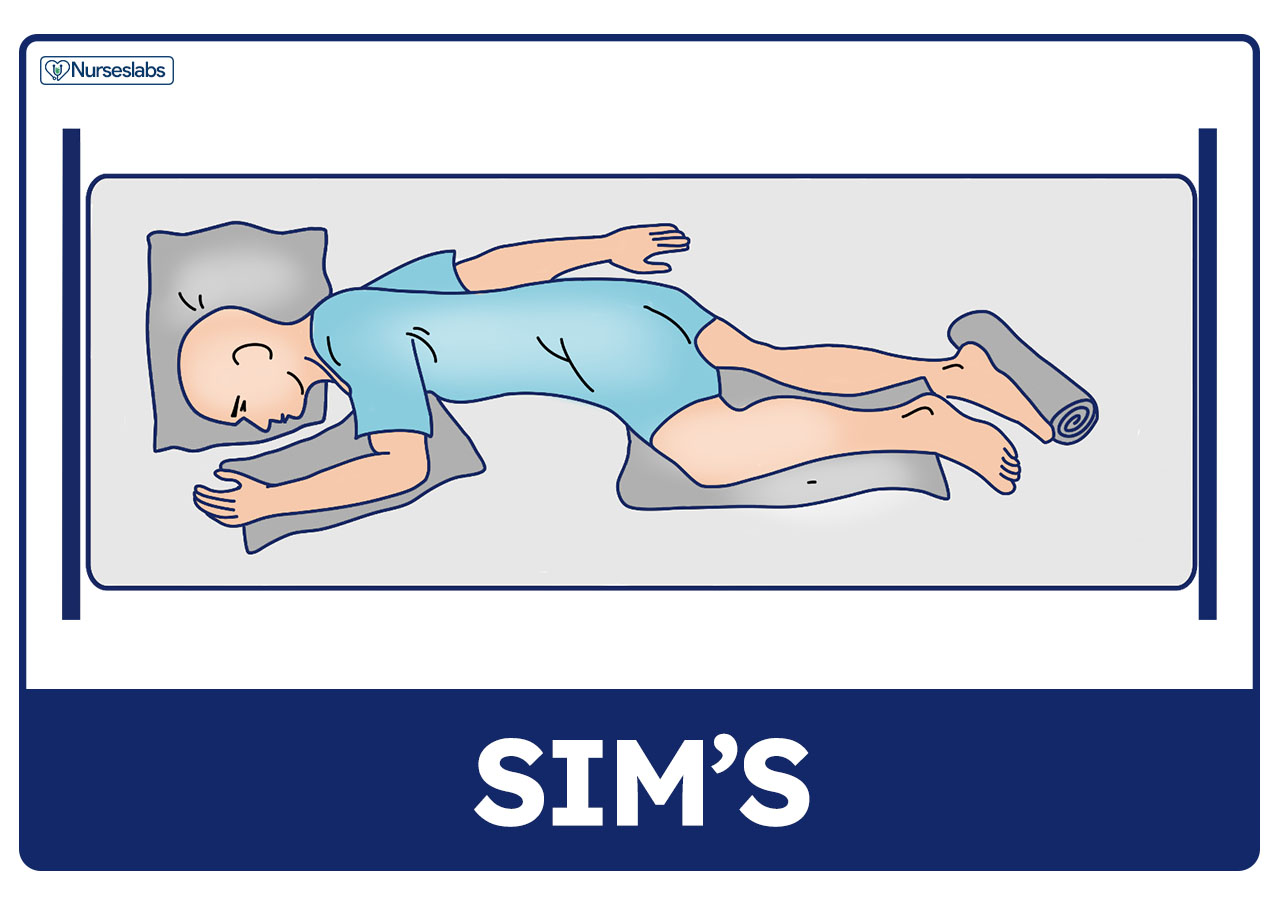


Patient Positioning Sims Orthopneic Dorsal Recumbent Guide



The Emergency Medicine Approach To An Unconscious Patient First10em
Following are guidelines for improving the arousal of the comatose patients Approaching the Patient • Make the patient identify you • Talk to the patient slowly and in a normal tone of voice • Keep sentences short and give the patient extra time to think about what you have said and repeat it a few times*Decorticate Posture is the position of a comatose patient where the arms are rigidly flexed at the elbows and wrists The legs also may be flexed with toes rigidly pointed The decorticate posture indicates a lesion in the brain In some instances the posture may be produced by applying a painful stimulus to a comatose patientA position in which the patient is placed on the left side with the left arm moved aside and supported to allow for lung expansion and the right leg crossed over the left This position affords the unconscious, breathing patient the best protection from airway occlusion or aspiration of fluids into the lungs See also position


Current Clinical Approach To Patients With Disorders Of Consciousness


Approach To The Comatose Patient
A fully conscious patient has a Glasgow Coma Score of 15 A person in a deep coma has a Glasgow Coma Score of 3 (there is no lower score) The Rancho Level of Cognitive Functioning Scale (LCFS) is a scale used to assess cognitive functioning in people with brain injury 11 The first three levels are similar to the stages of coma, VS, and MCS This scale is most often used in the first yearA change in the patient's position or administering medication to dry the secretions can help to reduce the sound, but may not completely eradicate it What is CheyneStokes breathing?Lawyers for the comatose woman who was raped and later gave birth at Hacienda Healthcare in Phoenix, Arizona have said she was raped repeatedly and may have been impregnated before


Repositioning Patients To Prevent Pressure Injuries Shield Healthcare


A Comprehensive Review Of Prone Position In Ards Respiratory Care
Once patient is on her side, pull both knees forward a bit, with the top knee higher than the bottom Put a pillow between the knees, calves and under the top foot, to keep the pressure off the



How Science Found A Way To Help Coma Patients Communicate Neuroscience The Guardian



After Stroke 3 Bed Positions You Will Want To Know And Follow Youtube



Safest Position For An Unconscious Patient Medscape Connect



Coma A Systematic Approach To Patient Evaluation And Management 03 05 19 Ahc Media Continuing Medical Education Publishing



1 428 Coma Patient Photos And Premium High Res Pictures Getty Images
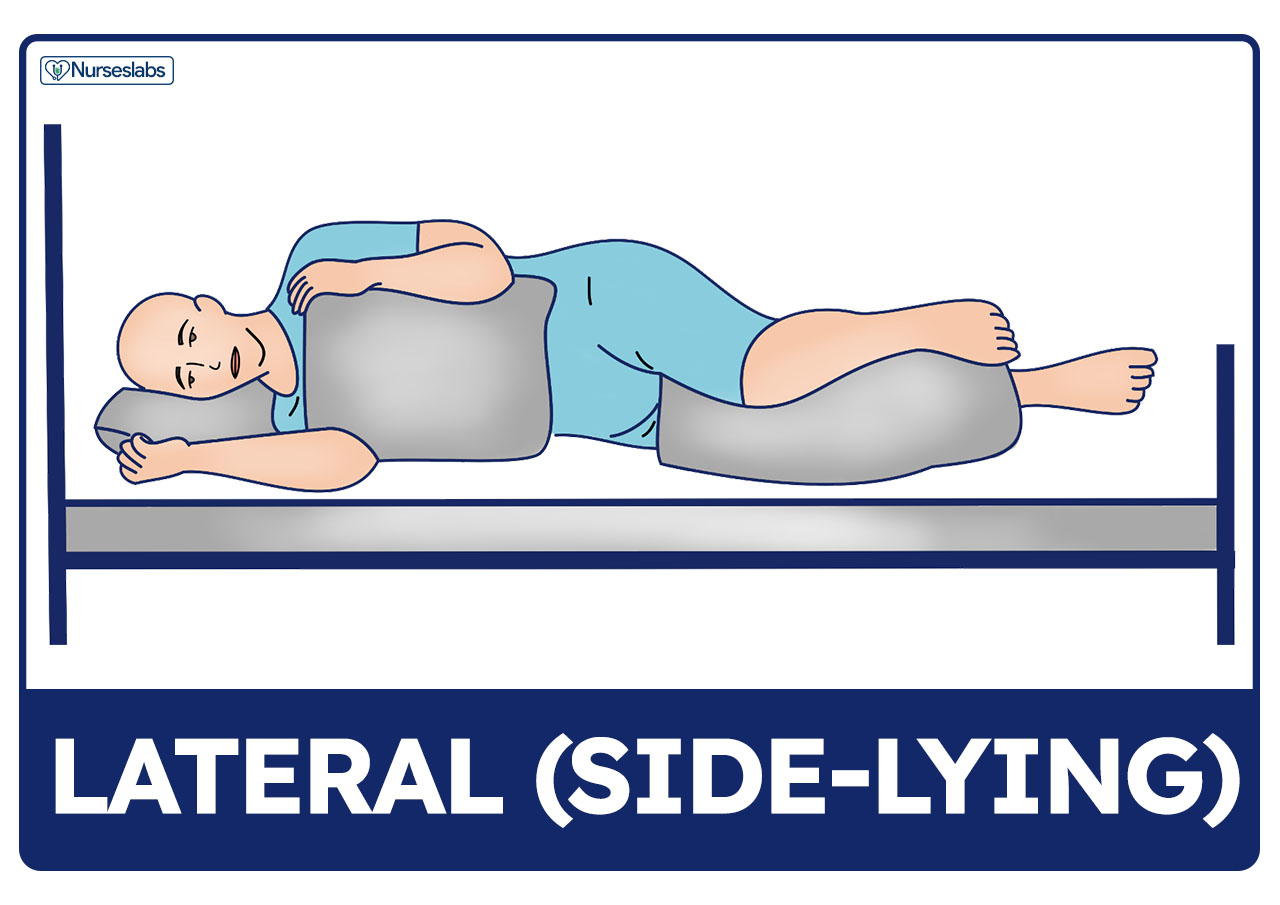


Patient Positioning Sims Orthopneic Dorsal Recumbent Guide



Delayed Recovery Of Consciousness After General Anaesthesia Bja Education



Neurological Assessment Of Coma Journal Of Neurology Neurosurgery Psychiatry



How Can We Tell If A Comatose Patient Is Conscious Scientific American



Serum Potassium Levels In Diabetic Coma Nejm



Objectives 44 U
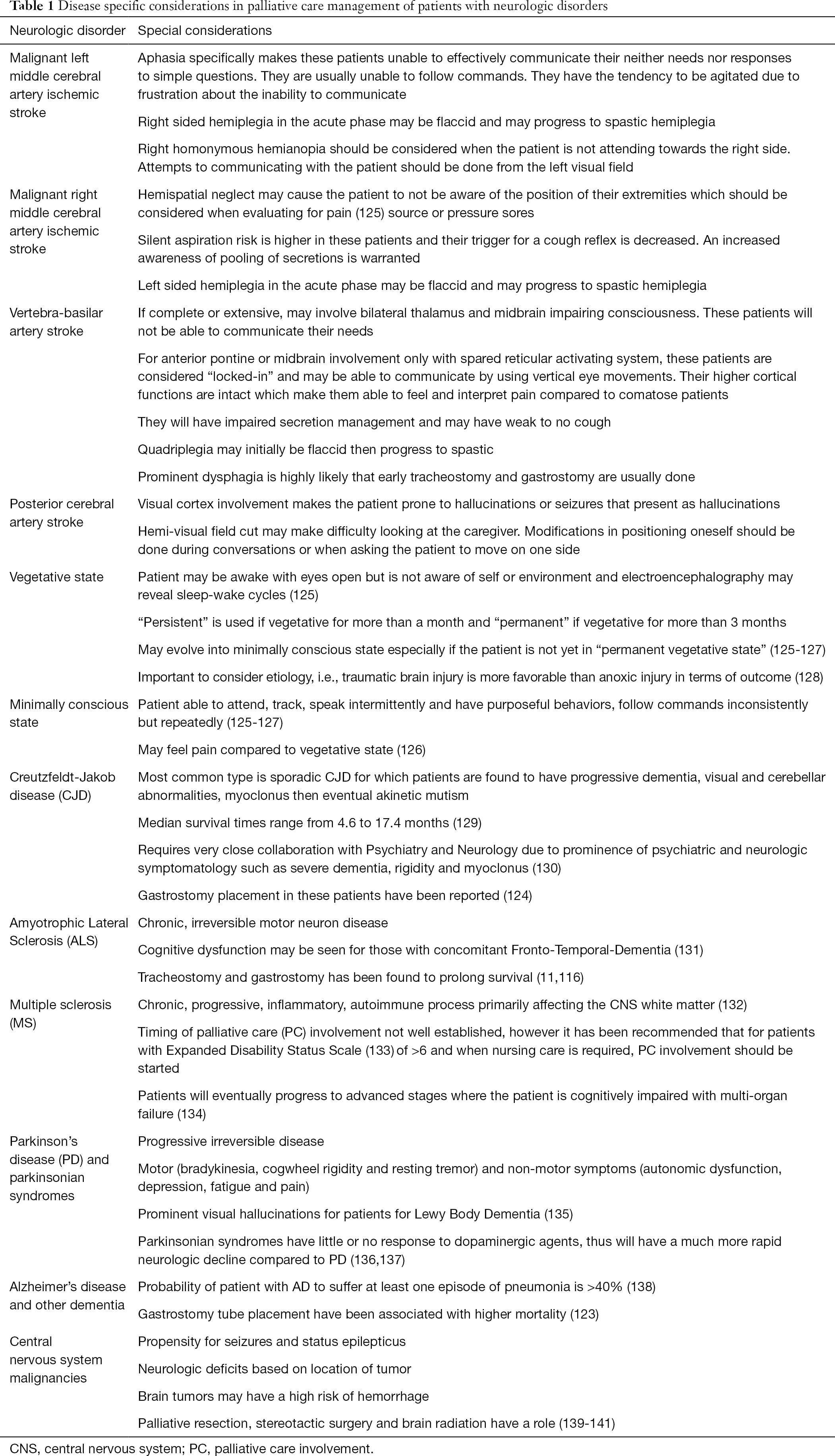


Challenges And Ethical Issues In The Course Of Palliative Care Management For People Living With Advanced Neurologic Diseases Sreenivasan Annals Of Palliative Medicine
2-1.png)


Table 2 2 From Neurological Examination Of The Unconscious Patient Semantic Scholar


A Comprehensive Review Of Prone Position In Ards Respiratory Care



Effect Of Prone Positioning During Mechanical Ventilation On Mortality Among Patients With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Cmaj



Effect Of Auditory Stimulation On The Level Of Consciousness In Comatose Patients Admitted To The Intensive Care Unit A Randomized Controlled Trial Article Nursingcenter



Rats Nibble Right Eye Of Coma Patient At Bal Thackeray Trauma Care Hospital In Mumbai Youtube



Sleeping Positions What S The Best Sleeping Position



6 Unconscious Patient Care



Normal Mri In A 19 Year Old Patient With Coma A B Sagittal And C Download Scientific Diagram



How Science Found A Way To Help Coma Patients Communicate Neuroscience The Guardian



Patient Positioning Cheat Sheet
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Recovery-56a2f6293df78cf7727b4d8e.jpg)


Recovery Position In First Aid Treatment



Approach To The Comatose Patient
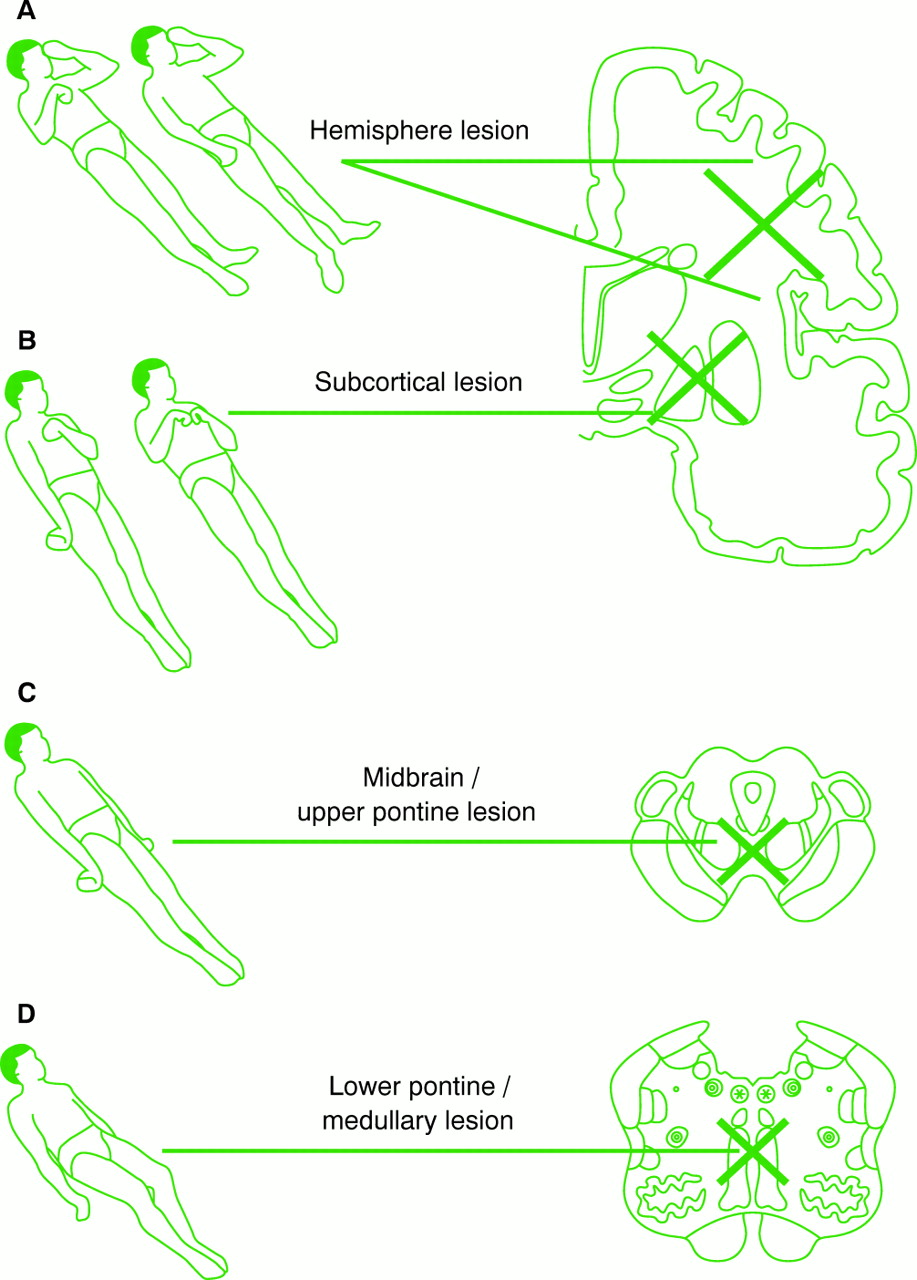


Neurological Assessment Of Coma Journal Of Neurology Neurosurgery Psychiatry
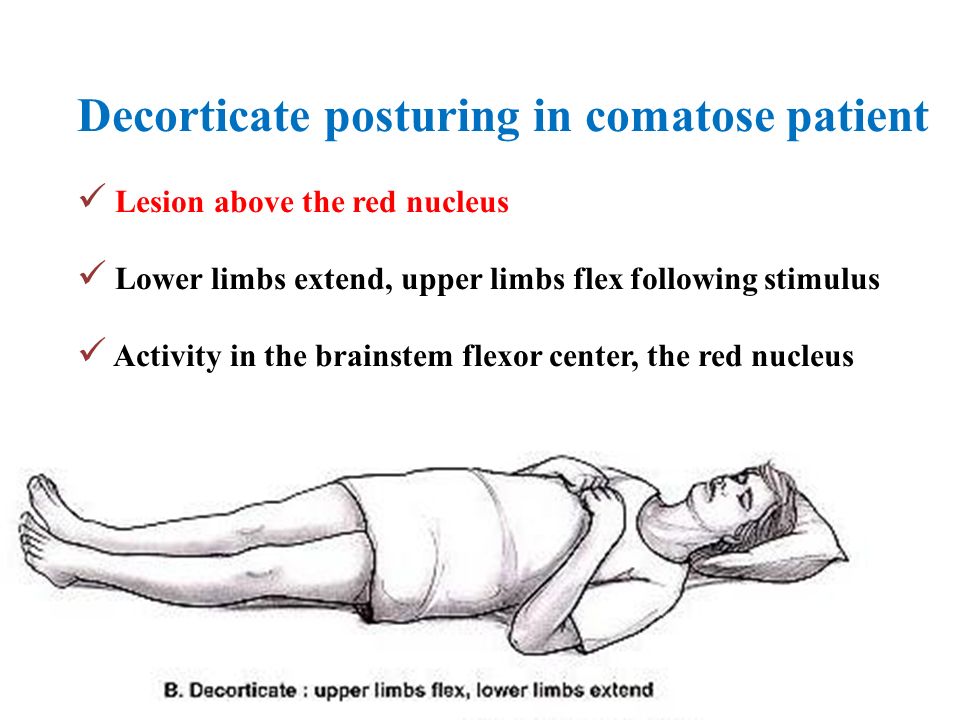


Approach To Coma Ppt Video Online Download



Coma Position Stock Photo Alamy



Unconsciousness An Overview Sciencedirect Topics


Repositioning Patients To Prevent Pressure Injuries Shield Healthcare



Prone Position As Prevention Of Lung Injury In Comatose Patients A Prospective Randomized Controlled Study Semantic Scholar


How To Perform A Lumbar Puncture
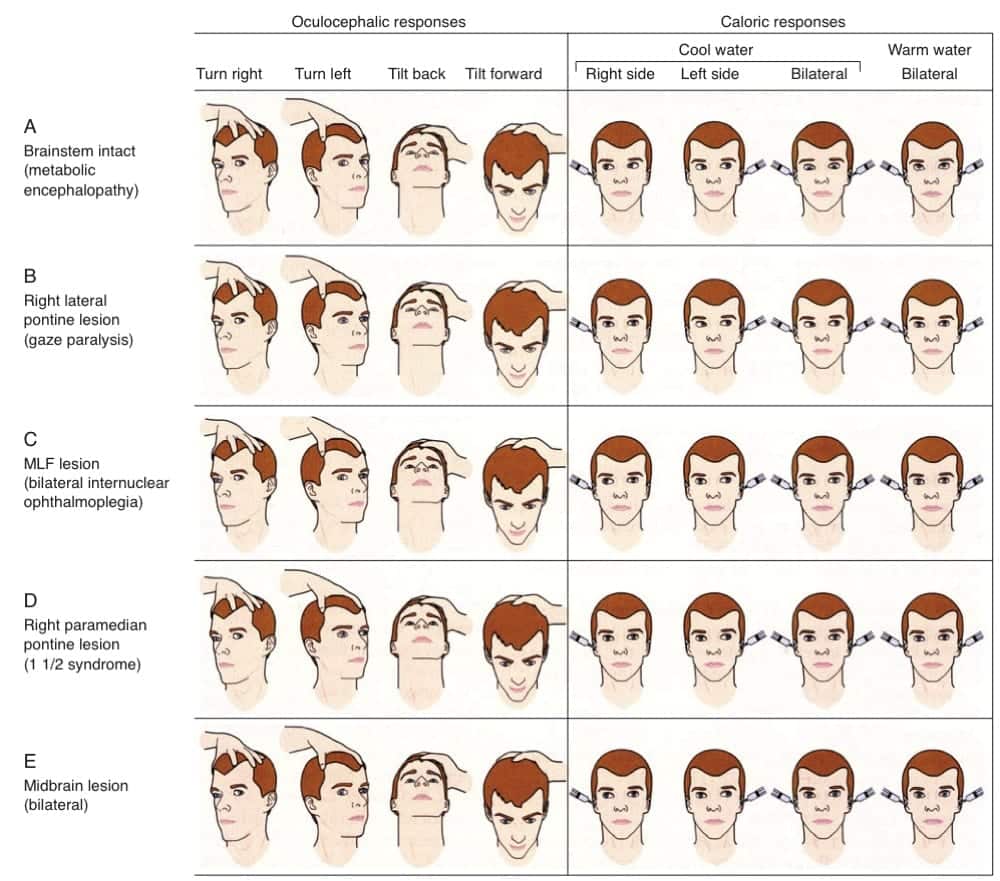


Examination Of The Unconscious Patient Litfl Ccc



Approach To The Comatose Patient



Coma What Is A Coma Patient


Is The Supine Position Associated With Loss Of Airway Patency In Unconscious Trauma Patients A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis Scandinavian Journal Of Trauma Resuscitation And Emergency Medicine Full Text



Teen Explains What Life Is Like In A Coma Abc News


Coronavirus Lying Icu Patients Face Down Boosts Survival Odds Daily Mail Online



What Is The Recovery Position In First Aid First Aid For Free



Approach To The Comatose Patient


Patient All Sensors Put The Pressure On Us


Glasgow Coma Scale Gcs How To Assess Gcs Geeky Medics



Position Of 67 Patients On Five Step Scale Of Susceptibility To Download Table


The Neurological Assessment Of The Critically Ill Patient Chapter 1 Neurocritical Care



Low Tech Way To Help Some Covid Patients Flip Them Over The New York Times



Common Questions And Answers About Severe Brain Injury What



Eye Movements Coma And Pseudocoma Litfl Neuro Mind Boggler
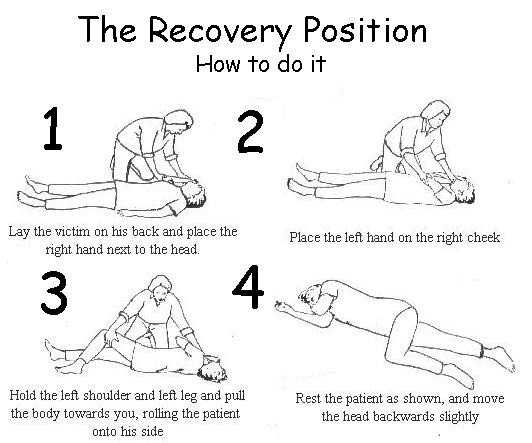


Diy First Aid Coma
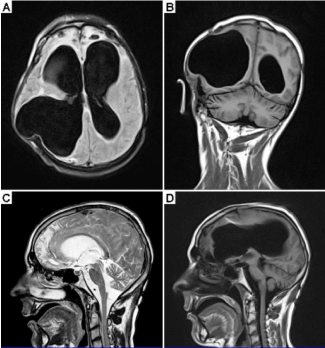


Permanent Coma Patient Re Learned To Speak Via Coordination Dynamics Therapy



Head Position In The Earl Y Phase Of Acute Ischemic Stroke An International Survey Of Current Practice Semantic Scholar



Approach To The Comatose Patient



Approach To A Child With Coma Ppt Video Online Download
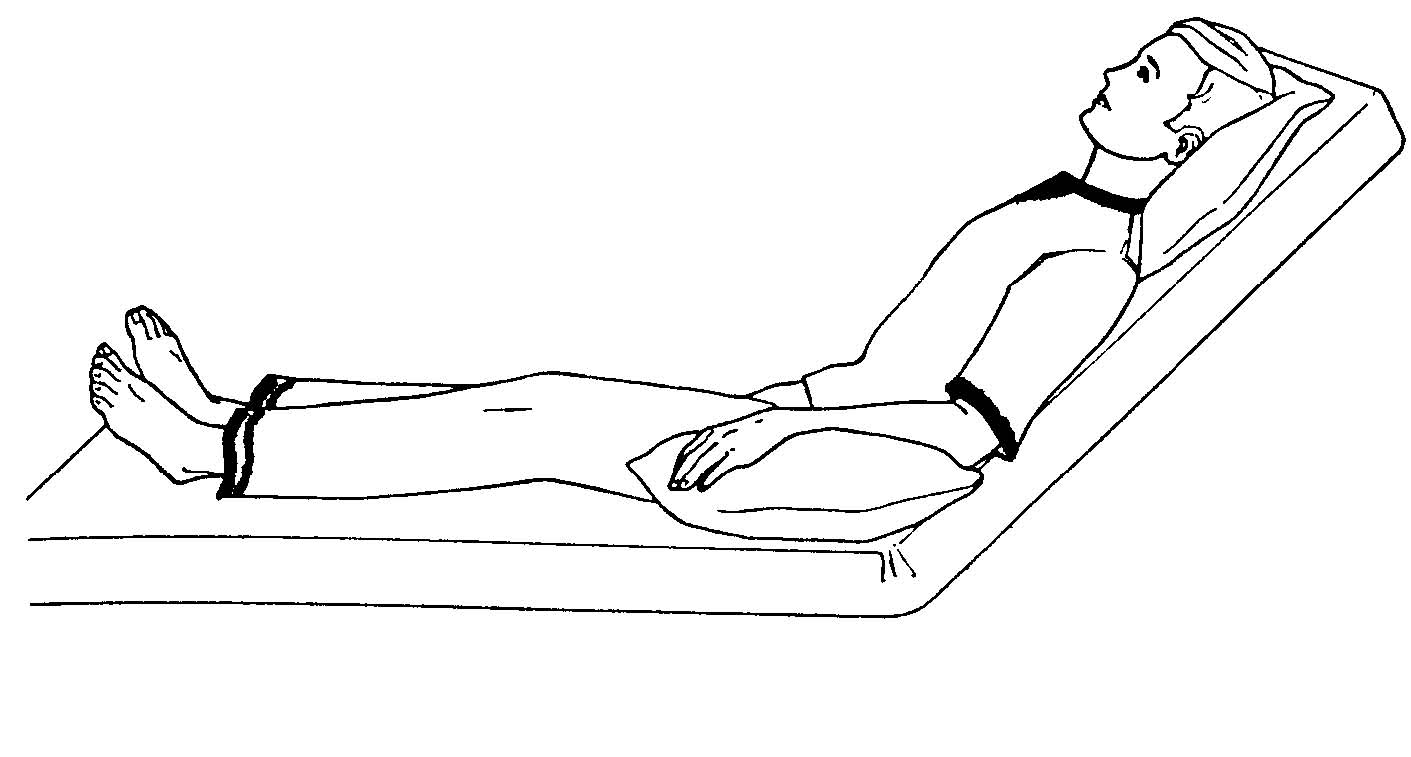


Recovery Room Care Of The Surgical Patient Multimedia Edition
/doctor-and-nurse-talking-with-patient-in-hospital-bed-906007066-5c0fc1b84cedfd00012c9773.jpg)


How To Properly Position Bed Bound Patients



1 934 Coma Illustrations Clip Art Istock






How Do Doctors Treat Coma Patients How Comas Work Howstuffworks



Correction Of Coma By The Lens And Position Of Contact Lens From Pupil Download Scientific Diagram



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿